Search results
Search for "Lewis base" in Full Text gives 57 result(s) in Beilstein Journal of Organic Chemistry.
Ligand effects, solvent cooperation, and large kinetic solvent deuterium isotope effects in gold(I)-catalyzed intramolecular alkene hydroamination
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 479–496, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.43
- effect of MeOH co-solvent on the 1a → 3a transformation was due to its role as a hydrogen bonding donor (proton source), or due to its role as a hydrogen bonding acceptor (Lewis base) [44]. To this end, we examined the impact of different alcohols (varied acidity and polarity) and different non-protic
- nitrogen. Thus, the rate of intramolecular hydroamination is enhanced by a more nucleophilic nitrogen. Another qualitative interpretation is that rates are enhanced by carbonyl basicity. Gas-phase basicity measurements indicate that ureas are more basic than amides [47][50], and here the most Lewis base
Using the phospha-Michael reaction for making phosphonium phenolate zwitterions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2024, 20, 41–51, doi:10.3762/bjoc.20.6
- reactive in chloroform solution, while in methanol the corresponding phosphonium phenolate is formed. Keywords: Lewis-base catalysis; Michael acceptor reactivity; phospha-Michael reaction; phosphonium phenolate zwitterion; Introduction Organocatalysis has emerged in recent years as a valuable and
- powerful tool for performing organic reactions [1] and polymerizations [2]. In this context phosphines have proven to be potent Lewis-base catalysts [3][4] for a variety of reactions [5], including but not limited to Rauhut–Currier [6], Morita–Baylis–Hillman [7], and Michael reactions [8][9][10]. In all
- -carbonyl-based Michael acceptors. Results and Discussion Synthesis During our endeavors to identify potent Lewis-base catalysts for the oxa-Michael reaction [13][14], the triarylphosphine 1 was tested in a model reaction (2 equiv allyl alcohol, 1 equiv acrylonitrile, 0.05 equiv 1). However, no conversion
Construction of diazepine-containing spiroindolines via annulation reaction of α-halogenated N-acylhydrazones and isatin-derived MBH carbonates
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1923–1932, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.143
- depicted in Scheme 5. At first, MBH carbonates of isatin 2 is attacked at the α-position by the Lewis base to give the ammonium salt A with elimination of carbon dioxide and a tert-butoxide ion. Secondly, the ammonium salt A is deprotonated by the in situ generated tert-butoxide ion to give the allylic
- elimination of a proton and the Lewis base. Obviously, the spiro compounds 5 and 7 are formed by a similar reaction mechanism. Additionally, the method was applied to a gram-scale reaction of α-halogenated p-toluenesulfonylhydrazone 6c and MBH nitrile of isatin 2c under the standard conditions (Scheme 6). The
Trifluoromethylated hydrazones and acylhydrazones as potent nitrogen-containing fluorinated building blocks
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1741–1754, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.127
- pairs and provides a good basis and scope for further extensions and explorations [39] (Scheme 3). Based on the work by Wu et al. and extending their previous work, Rueping and co-workers explored the effects of fluorine in organocatalytic reactions. They developed an asymmetric Brønsted acid–Lewis base
- Brønsted acid-assisted Lewis base catalysis. Synthesis of CF3-pyrazoles and CF3-1,6-dihydropyridazines. Asymmetric reactions of trifluoromethylimines with organometallic reagents. Mannich-type reaction of trifluoroacetaldehyde hydrazones. Synthesis of trifluoromethylated hydrazonoyl halides. Early work of
N-Sulfenylsuccinimide/phthalimide: an alternative sulfenylating reagent in organic transformations
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1471–1502, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.106

- azepane. A possible mechanism was suggested for this Lewis base catalysis system. Methanesulfonic acid (MsOH) activated reagent 14, which coordinated with the Lewis base (S)-E, to form complex I. Then, the transfer of the sulfenium ion to the alkene resulted in chiral thiiranium ion II. Capture of the
- enantioselectivity and the product yield were reduced. Although, the authors did not further explain the catalytic pathway. The use of organocatalysts in sulfenylation of N-heterocyclic compounds was investigated by Gustafson′s group in 2017 (Scheme 48) [81]. In their work, a series of conjugate Lewis base Brønsted
- acid organocatalysts were evaluated for sulfenylation on C3, or C2 position of N-heterocycles 115, including indoles, peptides, pyrrole, and 1-methyl-1H-pyrrolo[2,3-b]pyridine. The authors hypothesized a mechanism for the activation of N-sulfanylsuccinimides 1 or 14 by conjugate Lewis base Brønsted
Exploring the role of halogen bonding in iodonium ylides: insights into unexpected reactivity and reaction control
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 1171–1190, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.86

- reactions in processes that are typically metal-mediated, as well as the reactions observed between iodonium ylide-Lewis base pairs, including single electron transfers and proton transfers. As iodonium ylides exhibit two σ-holes, they offer two potential sites for halogen bonding to occur, potentially
- pattern shown in Figure 1, where R is the host atom or functional group to which the halogen is covalently bound, where X is the halogen atom possessing the σ-hole (halogen bond donor), and where Y is the Lewis base (halogen bond acceptor) [31]. σ-Holes arise from anisotropic covalent bonds between the
- such that they can undergo intramolecular reactions within the iodine’s ligand sphere. These EDA complexes have been proposed to then undergo single electron transfers from the Lewis base to the ylide, under both thermal or blue LED irradiation conditions, leading to C–H insertion products. Irradiating
Group 13 exchange and transborylation in catalysis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2023, 19, 325–348, doi:10.3762/bjoc.19.28
- loses dihydrogen to give a neutral borane 12, followed by B–C(sp2)/B–H transborylation with HBpin (ΔG‡ = 14.7 kcal mol−1) to give the borylated arene 13 and regenerate the catalyst (Scheme 4a). Fontaine showed that the steric bulk of the Lewis base had a significant effect on the rate of the reaction
A one-pot electrochemical synthesis of 2-aminothiazoles from active methylene ketones and thioureas mediated by NH4I
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 1249–1255, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.130
- can act as a bi-functional organocatalyst due to the existence of both Lewis base (NH2) and Brønsted acidic (COOH) sites. In the suggested mechanism, the carboxy group may polarize the carbonyl group of the active methylene ketone and the amino group as a Lewis base serves the formation of enolate to
Post-synthesis from Lewis acid–base interaction: an alternative way to generate light and harvest triplet excitons
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 825–836, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.83

- ; fluorescence; Lewis acid; Lewis base; post-synthesis; Introduction Organic light emitting diodes (OLEDs) show great potential to dominate the next generation of flat-panel displays and efficient light sources attributed to the advantages of self-illumination, high efficiency, wide color gamut, and flexibility
Bioinspired tetraamino-bisthiourea chiral macrocycles in catalyzing decarboxylative Mannich reactions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 486–496, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.51
- anion binding property and potent electrophilic activation ability [31][32][33][34][35][36]. To incorporate extra functionality, tertiary amine groups can be also embedded as Lewis base sites for realizing electrophilic/nucleophilic cooperative catalysis [37][38][39]. For this purpose, one kind of
- linking components to afford Lewis base sites and also for introduction of chirality. Different alkyl substituents including methyl, n-propyl, isopropyl, and 3-pentyl were incorporated in order to tune the size and steric effect of the macrocyclic cavity and thus to enable diverse cavity environments
New advances in asymmetric organocatalysis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2022, 18, 240–242, doi:10.3762/bjoc.18.28

- many reactions and a variety of organocatalysts can engage with them [18]. Nine excellent research articles within this special issue demonstrate the current state of the art in asymmetric organocatalysis. Chiral isothioureas became useful Lewis base catalysts for various transformations. Weinzierl and
Direct C(sp3)–H allylation of 2-alkylpyridines with Morita–Baylis–Hillman carbonates via a tandem nucleophilic substitution/aza-Cope rearrangement
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2505–2510, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.167
- acetamides and acetates catalyzed synergistically by a metal acyclic iridium complex and a chiral Cu(I) complex [19]. Besides transition-metal-catalyzed allylic substitution reactions, Lewis-base-catalyzed allylic functionalizations using Morita−Baylis−Hillman (MBH) adducts as electrophilic allylic
- synergistic catalyzed allylic alkylation between electron-deficient 2-ethyl benzoxazoles and MBH carbonates by the combination of a Lewis base and a metal salt [24]. In their studies, although pyridine derivatives were also applicable in the reaction, the presence of a strong electron-withdrawing NO2 group
Halides as versatile anions in asymmetric anion-binding organocatalysis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2270–2286, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.145
- development of an enantioselective aza-Sakurai cyclization (Scheme 12) [70]. In this transformation, a chiral thiourea catalyst 58 with a dibenzothiophene functionality serves as a dual H-bond donor and Lewis base to facilitate the cyclization of hydroxylactams 56. Thus, indolizine and quinolidizine
- frameworks 57 were accessed in excellent yields up to 93% and enantioselectivities up to 94% ee. Increased aromaticity proved again to be essential for achieving high enantioselectivities. Additionally, Lewis base activation of the allylsilane substrates through the thiourea sulfur atom is proposed to be
- , and c) asymmetric Mannich synthesis of α-amino esters. Thiourea-catalyzed enantioselective polycyclization reaction of hydroxylactams 51 through cation–π interaction. Enantioselective aza-Sakurai cyclization of hydroxylactams 56 implicating additional cation–π and Lewis base activation
Catalyzed and uncatalyzed procedures for the syntheses of isomeric covalent multi-indolyl hetero non-metallides: an account
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 2102–2122, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.137
- synthesized the similar compound 40, using a catalytic Lewis acid Zn(NTf2)2 and stoichiometric Lewis base γ-picoline combination in n-butyronitrile as solvent (Scheme 7c) [61]. This electron-donating solvent and toluene in the former reaction acted as stabilizers to the electron-deficient silicon species in
Electron-rich triarylphosphines as nucleophilic catalysts for oxa-Michael reactions
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1689–1697, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.117

- aromatic rings with methoxy groups increases the pKa value from 1.31 (TPP) to 4.20 (TMTPP) (Figure 1). Methyl cation affinities (MCA) which can be used as descriptors for the nucleophilicity of a compound were calculated by Lindner et al. who suggested TMTPP (651.0 kJ/mol) to be a stronger Lewis base than
Methodologies for the synthesis of quaternary carbon centers via hydroalkylation of unactivated olefins: twenty years of advances
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 1565–1590, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.112
- diastereoselectivity in the synthesis of bicyclic compounds (dr > 20:1, Scheme 19, 37d, 37e, and 37g). Substrates containing Lewis base moieties (Scheme 19, 36k) were tolerated in the reported reaction conditions, thereby representing a synthetic gain over other olefin isomerization methodologies. An important feature
Metal-free glycosylation with glycosyl fluorides in liquid SO2
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 964–976, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.78
- –base (HSAB) theory the fluoride leaving group is considered to be a hard Lewis base [12][13]. Consequently, a series of fluoride-activating systems containing hard Lewis acidic centers have been published following the first report [7][14][15][16][17]. Among these promoters Sn(II) species (SnCl2–AgX, X
- does not depend on the configuration of the anomeric center of the glycosyl donor. This observation points to the formation of a solvent-separated ion pair (SSIP) between the oxocarbenium ion and a counteranion, for example, fluorosulfite. At the same time, according to the Lewis base properties
Synthetic reactions driven by electron-donor–acceptor (EDA) complexes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2021, 17, 771–799, doi:10.3762/bjoc.17.67
- spectroscopy shows that phosphono radicals could proceed throughout the reaction. A halogen bond (XB) is a noncovalent interaction formed between a halogen atom and a neutral or negatively charged Lewis base. It is a kind of weak intermolecular interaction analogous to a hydrogen bond and basically can be
Reactions of 3-aryl-1-(trifluoromethyl)prop-2-yn-1-iminium salts with 1,3-dienes and styrenes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 2064–2072, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.173
- reaction of trifluoroacetaldehyde hemiaminals with enolizable carbonyl compounds in the presence of a strong base [23], the reaction of aldiminium salts with (trifluoromethyl)trimethylsilane/Lewis base [24], and the preparation of secondary α-(trifluoromethyl)propargylamines from imines CF3CH=NR and
Fluorohydration of alkynes via I(I)/I(III) catalysis
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1627–1635, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.135
- Lewis base upon ligand exchange (Figure 5) [56]. This working hypothesis may also rationalise the deletion experiment (10), the recalcitrance of acetyl derivatives, and the striking reactivity disparity between amides (12/13) and the phthalimide derivative 16. Finally, to investigate the fate of water
Heterogeneous photocatalysis in flow chemical reactors
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 1495–1549, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.125

Synthesis, liquid crystalline behaviour and structure–property relationships of 1,3-bis(5-substituted-1,3,4-oxadiazol-2-yl)benzenes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2020, 16, 149–158, doi:10.3762/bjoc.16.17

- electron D–A concept may be regarded as Lewis base–Lewis acid type or charge-transfer. Based upon the above considerations, we could attribute the close proximity of fluorinated chains in conformation B to a throw space electron D–A intramolecular interaction between the perfluoroalkyl chains (electron
Fluorinated azobenzenes as supramolecular halogen-bonding building blocks
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 2013–2019, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.197
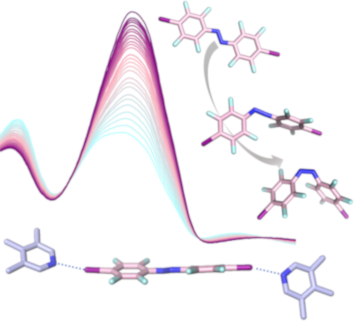
- noncovalent interaction between a polarized halogen atom (the halogen bond donor) and a Lewis base (the halogen bond acceptor) [1][2]. A prominent example regarding the origin of halogen bonding can be found in inorganic solid-state chemistry. The structurally diverse group of polyiodides, with its rich
Synthesis of polydicyclopentadiene using the Cp2TiCl2/Et2AlCl catalytic system and thin-layer oxidation of the polymer in air
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 733–745, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.69

- , which reacts with R-olefin and a Lewis base to form stable crystalline titanacyclobutanes. Both titanium carbene and titanacycles are ROMP catalysts (Scheme 4). PDCPD polymers were obtained by precipitation in ethanol, dried and characterized by FTIR, NMR, and GPC. Figure 6 displays a typical infrared
Sigmatropic rearrangements of cyclopropenylcarbinol derivatives. Access to diversely substituted alkylidenecyclopropanes
Beilstein J. Org. Chem. 2019, 15, 333–350, doi:10.3762/bjoc.15.29
- diastereoselectivity. However, the sigmatropic rearrangement of the highly hindered di(tert-butyl)phosphinite 6j and tetra(isopropyl) phosphorodiamidite 6k did not occur (Scheme 7) [37]. The mechanism proposed by Rubin et al. involves a reversible addition of the Lewis base (DBU) on the cyclopropene double bond at C2
- ’ would then be obtained and would eventually produce the diastereomeric phosphine oxides 7 and 7’. Computational studies indicated that the facial selectivity of the initial attack of the Lewis base (DBU) was not responsible for the observed diastereocontrol because of the low difference between the
- )-1f. Selective reduction of phosphine oxide (E)-3f. Attempted thermal [2,3]-sigmatropic rearrangement of phosphinite 6a. Computed activation barriers and free enthalpies. [2,3]-Sigmatropic rearrangement of phosphinites 6a–j. Proposed mechanism for the Lewis base-catalyzed rearrangement of phosphinites













































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































































